31 mayo, 2023
Sometimes companies have trouble figuring out the direct material price variance. Looking closely at these causes helps managers make better choices in the future. They can find ways to keep costs down and make sure they use resources well. Sharing variance reports and findings with relevant departments fosters a collaborative environment where everyone is aware of cost control objectives.
Direct Material Quantity Variance
For example, IoT sensors can monitor the exact amount of material used in each production cycle, allowing for precise adjustments and reducing waste. AI algorithms can analyze historical data to predict future material needs more accurately, helping businesses plan better and avoid unexpected variances. As the inventory is valued on standard cost, the material price variance must take the effect of the cost difference on entire quantity purchased during the period. This ensures 6 reasons to donate your car to charity that the entire gain or loss on the procurement of materials is reflected in the results of the current period. Evaluating material price variance is pivotal for a business, as it sheds light on the efficiency of purchasing activities and can signal areas for financial improvement. By honing in on this metric, organizations unlock insights into whether deviations from standard costs are working to their advantage or pointing to underlying issues in procurement processes.
Establish budgeted and actual price
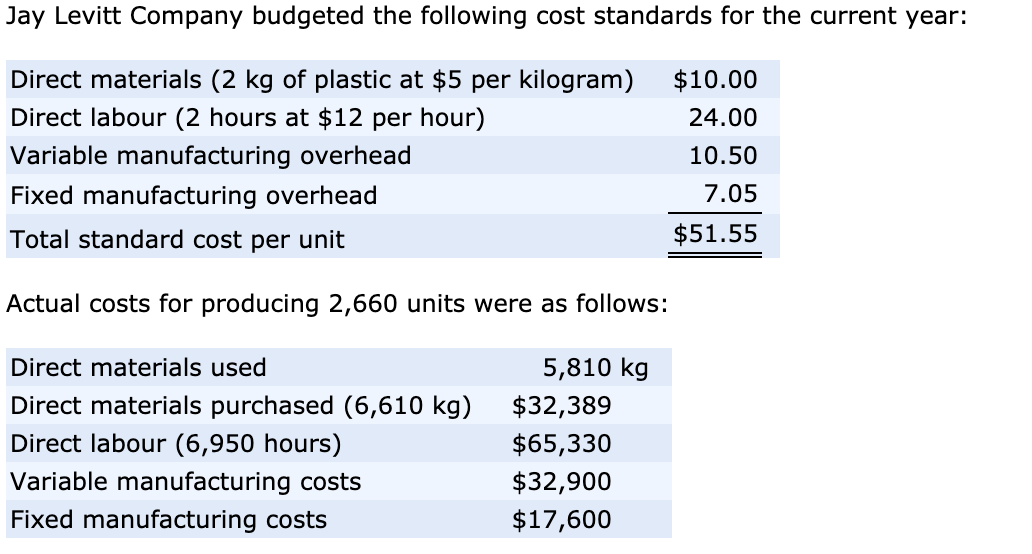
Let’s say your company set a budget of $5 for a pound of copper, but the market rates went up, and you ended up paying $6 per pound. To figure out the variance, subtract that actual price ($6) from the budgeted price ($5), giving you a difference of $1 per pound. In a multi-product company, the total quantity variance is divided over each of the products manufactured. If Fresh PLC values its stock on FIFO or other actual cost basis, then the variance may be calculated on the quantity consumed during the period.
What is meant by standard direct material usage?
For instance, procurement teams can work closely with suppliers to negotiate better prices, while production teams can implement process improvements to reduce material waste. This cross-functional collaboration ensures that all aspects of the business are aligned towards achieving cost efficiency. This setup explains the unfavorable total direct materials variance of $7,200 — the company gains $13,500 by paying less for direct materials, but loses $20,700 by using more direct materials. Material variance is the difference between the actual cost of direct materials and the expected cost of those materials. Direct materials quantity variance is also known as direct material usage or volume variance.
An adverse material price variance indicates higher purchase costs incurred during the period compared with the standard. Now that we have understood the direct material price variance calculation, let’s look at how to interpret it. Standard direct material usage refers to the amount of materials allowed to be used per unit produced. One more, the favorable variance may arise from the purchase of low-quality material. The purchasing department and production manager need to do proper inspect all the material during delivery.
You’ll need to gather data on the actual quantity of materials employed in production. Internal factors, such as production efficiency and waste management, significantly affect material quantity variance. Inefficient production processes, outdated machinery, or inadequate employee training can result in higher material consumption than planned.

The direct material price variance is the difference between the actual price paid to acquire a direct materials item and its budgeted price, multiplied by the actual number of units acquired. This information is needed to monitor the costs incurred to produce goods. Direct material price variance is the difference between actual cost of direct material and the standard cost.
Market conditions, geopolitical events, and changes in supply and demand can all cause fluctuations in material costs. For instance, a sudden increase in the price of steel due to international trade policies can lead to an unfavorable material price variance for manufacturers relying on this resource. Companies must stay informed about market trends and consider strategies such as hedging or long-term contracts to mitigate these risks.
- It tracks if spending goes as planned or if there are surprises needing attention.
- The direct material price variance is also known as direct material rate variance and direct material spending variance.
- The net direct materials cost variance is still $1,320 (unfavorable), but this additional analysis shows how the quantity and price differences contributed to the overall variance.
- The actual price must exceed the standard price because the material price variance is adverse.
An unfavorable variance, on the other hand, indicates that the amount of materials used exceeds the standard requirement. The purchasing staff of ABC International estimates that the budgeted cost of a chromium component should be set at $10.00 per pound, which is based on an estimated purchasing volume of 50,000 pounds per year. During the year that follows, ABC only buys 25,000 pounds, which drives up the price to $12.50 per pound.
This step is where you find out if you spent more or less than planned on materials. You calculate this price difference by subtracting the actual cost from the standard cost for each unit bought. To calculate the material price variance, you must first know how much product your company used.
Understanding direct material variance is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain cost efficiency and improve profitability. This concept involves examining the differences between expected and actual costs of materials used in production, providing insights into potential areas for financial improvement. To apply this method to the Band Book example, take a look at the next diagram. Direct materials actually cost $297,000, even though the standard cost of the direct materials is only $289,800. The actual quantity of direct materials at standard price equals $310,500. A favorable materials quantity variance indicates savings in the use of direct materials.
