7 agosto, 2024

Whether you’re a business owner, investor, or policymaker, understanding the PI can empower you to make informed choices about resource allocation and project selection. Investing in Archer will allow Garch Ltd to earn $80,000 in annual cash flow for the next 5 years. The projects require investments of $300,000; $200,000; and $600,000 for Archer, Brochure, and Catcher respectively. We’d say that for every £1 pound that you invest in A, you earn £1.50 in cash flow, in present value terms. The key takeaway here is that you can invest 1% of the requirement of Project B, by investing in Project A, and earn a higher Net Present Value per pound/dollar invested.
Profitability Index Formula
The profitability index measures the present value of future expected cash flows and the initial amount invested in a project. The PI, known as the value investment ratio (VIR) or profit investment ratio (PIR), represents the relationship between the costs and benefits of a proposed project. For example, a project with an initial investment of $1 million and a present value of future cash flows of $1.2 million would have a profitability index of 1.2. Based on the profitability index rule, the project would proceed, even though the initial capital expenditure required are not identified. The discounted payback period refers to the number of years it takes the cumulative discounted cash flows from a project to equal the original investment. By factoring in a discount rate, the discounted payback period is a slight improvement over the payback period.
Profitability Index Formula Explained (With Examples)
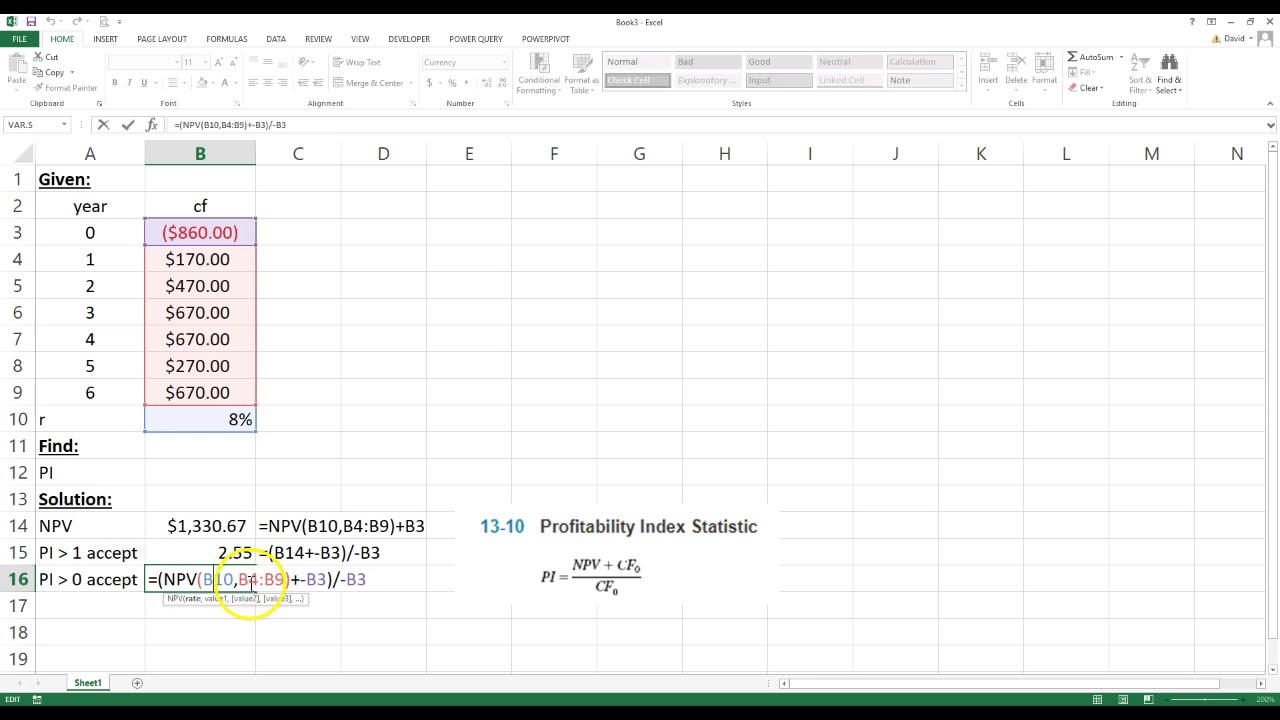
The Profitability Index (PI) measures the ratio between the present value of future cash flows and the initial investment. The index is a useful tool for ranking investment projects and showing the value created per unit of investment. To calculate NPV all, we need to do is to add up all discounted cash flows and then deduct the initial investment required.
Interpreting Profitability Index Values
- This is the present value of the future cash flow that you’re earning, for every pound you’ve invested.
- As we’ve explored, understanding the components and formula of PI is crucial for any finance professional or business leader.
- Learn from instructors who have worked at Morgan Stanley, HSBC, PwC, and Coca-Cola and master accounting, financial analysis, investment banking, financial modeling, and more.
- A profitability index number might be 1.5, but you wouldn’t necessarily know the capital expenditure required.
The profitability index allows investors to quantify the amount of value created per unit of investment. Using the profitability index formula, and setting the present value of future cash flows (PV) equal to the initial investment (I), we get the following. The profitability index is sometimes referred to as the value investment ratio. Where “PV of future cash flows” is the present value of cash flows, starting from period 1 until the end of the project, and NPV denotes the Net Present Value.
Now we assume that John Brothers can undertake only one of these two projects. The net present value analysis favors project 1 because its NPV number is bigger than project 2. But the profitability index indicates repaying the 2008 first otherwise and says that project 2 with its higher PI value is a better opportunity than project 1. As the value of the profitability index increases, so does the financial attractiveness of the proposed project.
It works as a way for you to appraise a project to make a more informed decision. To find more attractive investments, look for a profitability index that is the highest. This shows that the project will generate value for your business and it can be a good investment. The higher a profitability index means a project has benefits and would be considered more attractive. It can be very helpful in ranking potential projects in order to let investors quantify their value.
Even when a project offers a high net present value, it may still be passed over based on the use of other financial calculations. The present value of future cash flows is a method of discounting future cash to its current value, and requires the implementation of the time value of money calculation. This discounting occurs because the current value of $1 is not equivalent to the value of $1 received in the future. Money received closer to the present time is considered to have more value than money received further in the future.
The Net Present Value (NPV) of a project is the potential change in wealth resulting from the project after accounting for the time value of money. The NPV for a project with one investment outlay made at the start of the project is defined as the present value of the future after-tax cash flows minus the investment outlay. As we’ve explored, understanding the components and formula of PI is crucial for any finance professional or business leader.
This article will provide a detailed guide for calculating PI, how to use it, and the difference between profitability index vs. NPV and other valuation metrics. When it comes to making investment decisions, businesses are faced with the challenge of determining which projects will yield the most significant returns. One of the tools at their disposal is the Profitability Index (PI), a financial metric that helps investors and companies assess the desirability of an investment or project. In this article, we will delve into the definition of the Profitability Index, explore its key components, and break down the formula used to calculate it. By understanding PI, businesses can make more informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
You will then have to make a decision on what’s going to be best for your business moving forward. The result can be a higher return on investment and an increase in potential profitability. Regardless of the type of business you operate or your industry, generating a profit is critical to growing and expanding. And when it comes to projects or possible investments, understanding the benefits you can receive is important. When applying the PI technique to check on the profits expected from a project, it is recommended to not consider the size of the project.
In the case of limited funds, we should rank projects according to profitability index (PI) ratios and not on the basis of their net present values (NPVs). Since project 2 and 3 both have higher PI values than project 1, they should be ranked ahead of project 1 while rationing the available capital. The NPV method reveals exactly how profitable a project will be in comparison to alternatives. When weighing several positive NPV options, the ones with the higher discounted values should be accepted. The profitability index rule is a decision-making exercise that helps evaluate whether to proceed with a project.
